What would you do if someone presented you with a sequence of numbers without context? There is a possibility that some people may attempt to begin addressing the issue by focusing on its Order. Still, in mathematics, this is not an efficient method for problem-solving.
The ancient Romans and Greeks were well aware of the significance of developing a method that could be used to solve mathematical issues. This technique assisted in navigation all around the globe and in astronomers’ mapping of the sky. Nevertheless, there was always a system in place, which was true regardless of what it was.
Many industry professionals aren’t convinced that the sequence of operations was “created” in the strictest sense of the word. Instead, it was adopted as a standard method of solving mathematical problems because it simply made sense.
Importance of Order Of Operations
When solving an equation, there is a particular order in which specific rules need to be applied, and this Order is referred to as the Order of operations. Evaluating any mathematical statement, which may include arithmetic operations such as division, multiplication, addition, or subtraction, is called operations in mathematics.
When we say “operations,” we mean the procedure we just described. Let’s go through the rules for the sequence of operations in great detail and see how well we can recall them using memory techniques that are just a few words long.
The Order of Operations is a rule in mathematics that states we evaluate the parentheses or brackets first, the exponents or the guidelines second, division or multiplication third, and addition or subtraction last. The rule states that we evaluate the parentheses or brackets first because they are located at the beginning of the mathematical expression (from left to right, whichever comes first).
In mathematics, simplifying an expression after an evaluation might provide a variety of distinct outcomes because the review may include many operations. However, there is only ever going to be one solution that is appropriate for each given phrase. We take any mathematical expression and apply a particular set of principles to simplify it and arrive at the proper result.
These principles center on the fundamental mathematical operators employed across the field. Addition (plus sign), subtraction (minus sign), division (tilde), and multiplication (square brackets) are all examples of operators. Look at the picture provided to get an idea of the sequence of operations.
How To Define Order Of Operations?
As was just said, the Order of operations is a fundamental set of principles of precedence that must be followed when resolving any mathematical equation that involves more than one operation. If an expression has a subexpression sandwiched between two operators, the Order of the operators in the following list determines which operator should be applied first.
This is where the rules and the sequence of operations are expressed:
- All types of brackets, such as [], {}, and ()
- Exponents
- Divisions
- Multiplications
- Additions
- Subtractions
The previously described guidelines always differ following the various mathematical expressions used.
Rules For Order Of Operations
When carrying out any action on the many numbers represented by the expression, we shall stick to the fundamental guidelines laid out in the Order that they were presented.
Rule 1:
Take note of the manner of speech. You must first work out the sum of the numbers included inside the parenthesis or brackets. We go via grouping operations from the inside out.
Take note of the pattern of brackets that are included in the equation; there is a particular order to solve the parentheses, which is denoted by the notation [{()}]. First, you need to solve the problem using the round brackets (), followed by the curly brackets {}, and then the box brackets [].
The sequence of the operations included inside the parentheses must be followed.
Rule 2:
After you have solved the numbers included inside the parenthesis, search for any phrase represented by exponents and solve that one.
Rule 3:
Only the four fundamental operators are left to consider at this point. Find the numbers that need the multiplication or division operation, then go through the solutions starting at the leftmost column.
Rule 4:
Last but not least, search for any expressions that include addition or subtraction, and then solve those problems working from left to right.
PEMDAS and BODMAS
You may learn the rules by memorizing the PEMDAS or the BODMAS, which are distinct acronyms. These two names indicate the sequence that should be followed while performing the operations included inside an expression. The following is an explanation of the phrase for each letter used in the acronyms discussed. To start, we are going to talk about the PEMDAS.
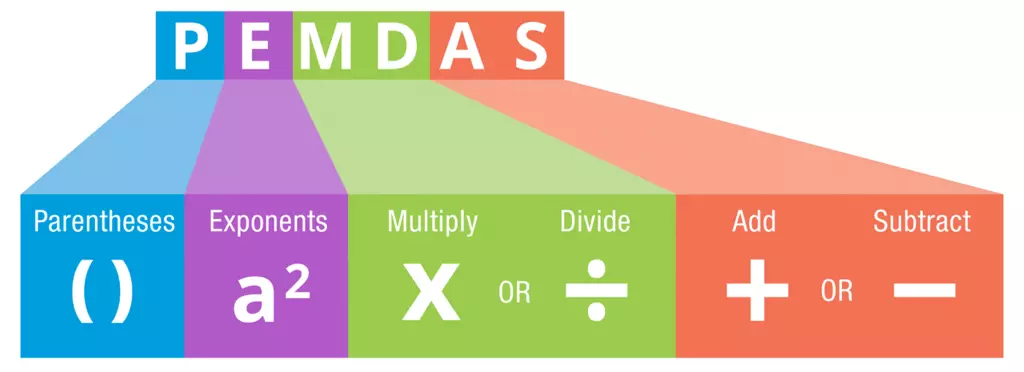
Order of PEMDAS:

P = Parentheses (), {}, []
E = exponents
M = Multiplications
D = Divisions
A =Additions
S = Subtraction
Order of BODMAS:
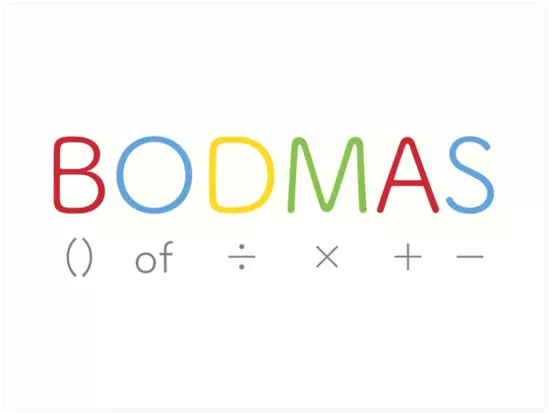
B = Brackets (), {}, []
O = Order
D = Divisions
M = Multiplications
A = Additions
S = Subtraction
PEMDAS even stands for ‘Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally’
Parentheses are denoted by the letter “P,” exponents by the letter “E,” multiplication by the letter “M,” division by the letter “D,” addition by the letter “A,” and subtraction by the letter “S” in the notation known as PEMDAS.
You may still utilize this strategy even if you don’t notice the operations following one another in the issue.
Remember to always do multiplication and division processes from left to right whenever they appear in a problem.
Please Excuse My Deal is not for you if you have no interest in it. If you need a phrase to help you remember PEDMAS, Aunt Sally, you can try “Popcorn Every Monday Drinks Always Saturday” or “People Everywhere Made Decisions About Sums.” If none of them appear to work, you’ll have to come up with your solution. When you have the sequence of operations ingrained in your memory, you will be prepared to take the algebra world by storm.
Tips To Remember The Order Of Operations
You have just taken in some information on the two distinct terms, PEMDAS and BODMAS. This is the most effective method for committing the Order of operations to memory. To help you recall PEMDAS, think about the sentence “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally.” The phrase “Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction” is what it refers to the sequence of operations.
Here, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are brought together. Similarly, we should be able to recall the sequence of operations using the acronym BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction.).
The following procedures should be carried out to understand the sequence of operations in the simplest possible way:
- Begin by clarifying the phrases that are included inside the brackets.
- Find the solution for the exponential terms.
- You may either divide or multiply the numbers.
- You may either add or subtract the numbers.
