A triangle is a kind of polygon that consists of three separate sides. The point at which two of the triangle’s sides meet to produce an interior angle is termed the vertex of the triangle. There is no such object or item as a triangle that does not have three sides, three vertices, and three internal angles.
Fundamental Properties of Triangles
- There are three internal angles in a triangle, and the combined degrees of those three angles add up to 180 degrees. This aspect of a triangle’s geometry is called the angle-sum property.
- There are three sides to a triangle. The sum of the sizes of any two of a triangle’s sides is greater than the length of any one of the triangle’s third sides. This concept is sometimes referred to as the triangle inequality property in certain circles.
- The side of the triangle on the opposite side to its most significant angle is the longest side, and the side of the triangle that differs from its smallest angle is the shortest side.
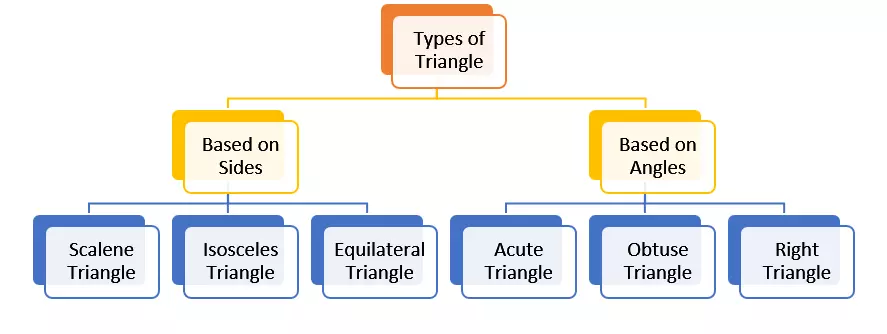
Types of Triangle
There are six distinct sorts of triangles, each being distinguished from the others based on the length and measure of the lines and angles composing the triangle, respectively. To refresh your memory, a triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles.
The wide varieties of triangles each have unique specifications and designs, and based on them, the qualities of triangles may be determined.
A triangle is known as a three-sided polygon that has three angles, as the name of this shape may imply. When all of the internal angles of a triangle are added together, the result is always 180 degrees. This aspect of triangles is referred to as the angle sum property.
In addition, a triangle has a variety of characteristics. Let’s go into some specifics regarding the different kinds of triangles.
- Based on Sides
- Based on Angles
Based on Sides
- Scalene Triangle
- Isosceles Triangle
- Equilateral Triangle
Scalene Triangle
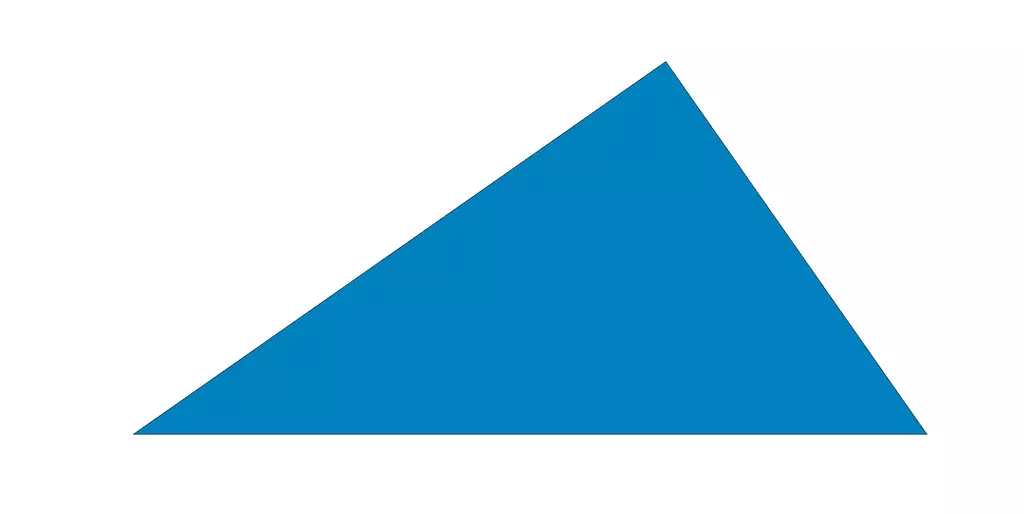
A scalene triangle is distinguished by the fact that each of its side lengths is of a distinct measurement. In a triangle of this kind, no single side will be the same size as any other.
All of the inner angles of a scalene triangle are distinct. The diagram that follows illustrates a scalene triangle. As can be seen, the lengths of none of the sides are the same.
Isosceles Triangle
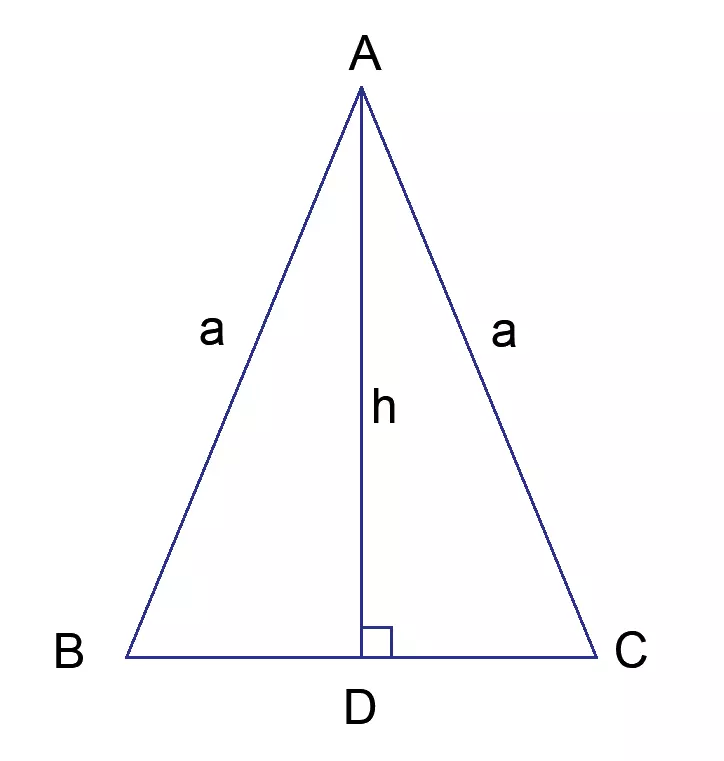
Two of the triangle’s three sides will have the same length in a triangle with isosceles proportions. Therefore, the angles that are opposed to the equal sides are equal.
To put it another way, the isosceles triangle has two sides equal in length and two angles equal. The following illustration depicts an isosceles triangle for your reference.
Equilateral Triangle
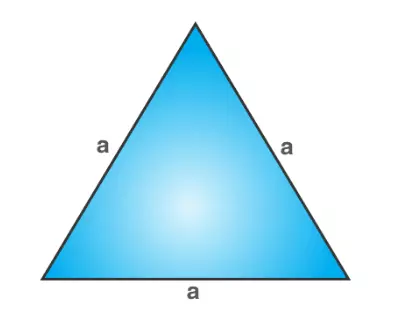
Each of the three sides will have the same length in a triangle with equilateral sides. In this scenario, the degree measurement of each inner angle will equal sixty degrees.
Since the three angles of an equilateral triangle are equal, this kind of triangle is occasionally referred to as an equiangular triangle. The diagram that may be seen below is an example of an equilateral triangle.
Based on Angles
- Acute Triangle
- Obtuse Triangle
- Right Triangle
Acute Triangle
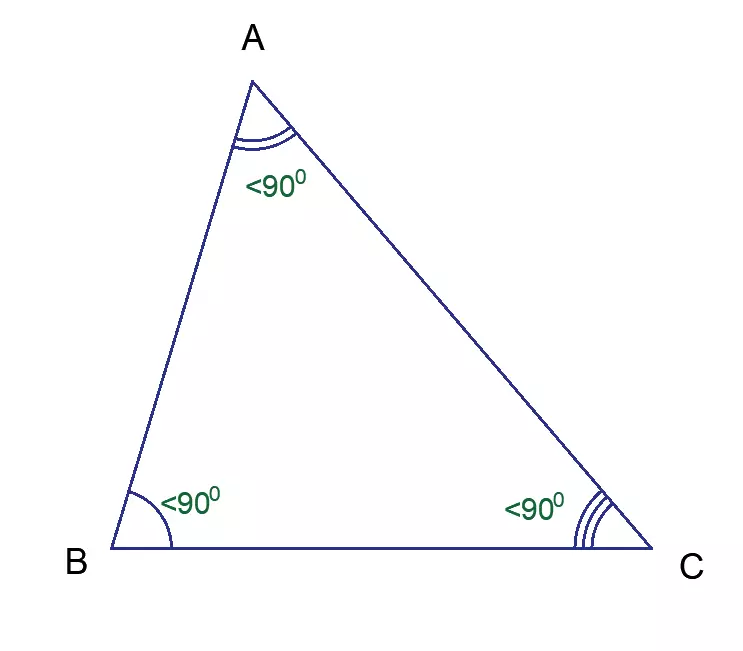
One definition of an acute triangle is that each triangle’s three inner angles are acute. On the other hand, each triangle’s internal angle is fewer than ninety degrees, and we say that the triangle has sharp angles. An illustration of an acute triangle may be seen in the following figure.
As shown in the above illustration, all of the inner angles of the triangle are less than ninety degrees, making it what is known as an acute triangle.
Obtuse Triangle
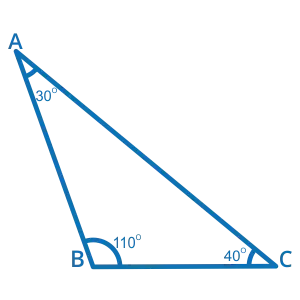
Triangles are said to be obtuse when one of the three internal angles has a measure that is more than 90 degrees. Obtuse triangles may be formed in a variety of ways. To put it another way, if one of the angles that make up a triangle is an obtuse angle, we refer to the whole triangle as an obtuse-angled triangle. The following illustration depicts an obtuse triangle for your reference.
One of the angles in the triangle that was just shown has a value of more than 90 degrees. As a result, it is a triangle with obtuse angles.
Right Triangle
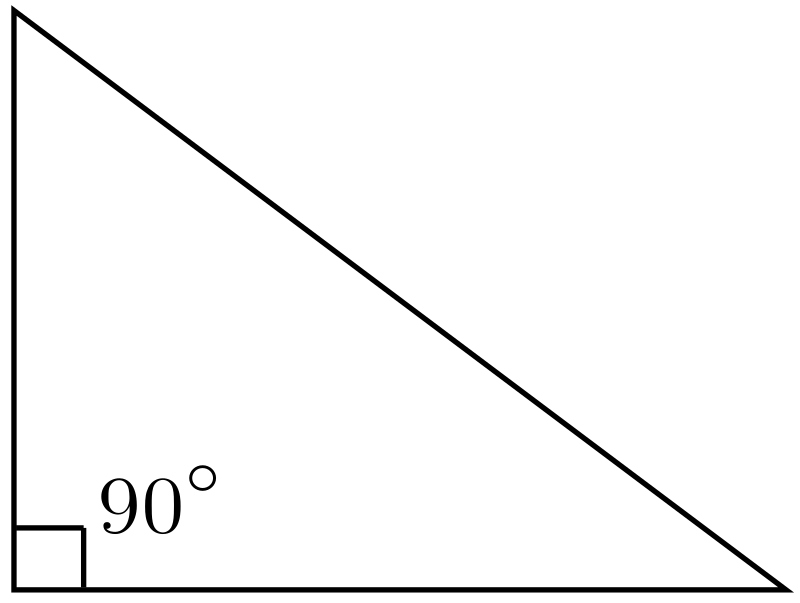
A triangle is considered a right triangle if its angles are precisely 90 degrees. In a triangle with a right angle, the side that is perpendicular to the right angle (the angle that is 90 degrees) will be the longest and will be referred to as the hypotenuse.
You could come across varieties of triangles with combined names like “right isosceles triangle” or something similar, but this only indicates that the triangle has two equal sides and that one of the internal angles needs to be 90 degrees. Because one of the triangle’s three angles is precisely 90 degrees, we refer to it as a right triangle.
